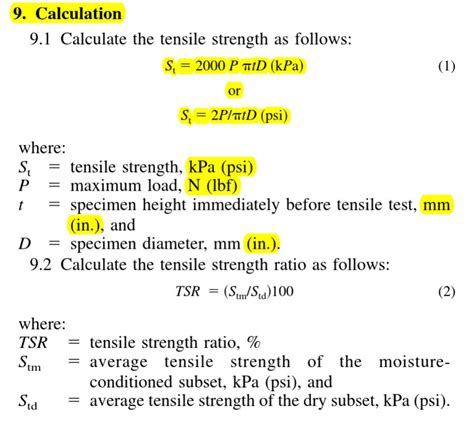
strain rate in tensile test|tensile strength formula and units : Brand ASTM standard E 8 requires that the rate of stress increase be controlled to between 1.1 and 11 MPa/sec when determining the yield point. In any case, the speed of test (strain rate, stress . Resultado da SHA1: 83c4d383e3679380c4cb0c1f27f11bfaedb7904b. 47.1.46. 2023-08-30. Changelog. MD5: b2ce7f1b4f06562a55cb0219f44949fb. SHA1: .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Sara estanislau | Lua santana. 81 members. @brasiloirinha. Open a Channel via Telegram app. Preview channel. Don't have Telegram yet? Open via web telegram.
tensile stress and strain formula
ski doo 850 compression test
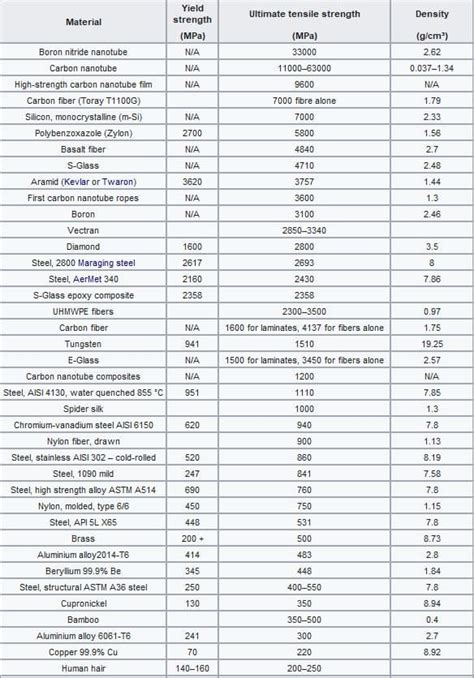
tensile strength of materials chart
Stress-strain curves are an extremely important graphical measure of a material’s mechanical properties, and all students of . See morePerhaps the most important test of a material’s mechanical response is the tensile test (Stress-strain testing, as well as almost all experimental procedures in mechanics of . See moreAs discussed in the previous section, the engineering stress-strain curve must be interpreted with caution beyond the elastic limit, since the . See more
ASTM standard E 8 requires that the rate of stress increase be controlled to between 1.1 and 11 MPa/sec when determining the yield point. In any case, the speed of test (strain rate, stress .Slow strain rate testing (SSRT), also called constant extension rate tensile testing (CERT), is a popular test used by research scientists to study stress corrosion cracking. It involves a slow (compared to conventional tensile tests) dynamic strain applied at a constant extension rate in the environment of interest. These test results are .Stress–strain curve typical of a low-carbon steel Stress–strain curve for a tensile test In engineering and materials science . For strain less than the ultimate tensile strain, the increase of work-hardening rate in this region will be .
%PDF-1.5 %âãÏÓ 1381 0 obj > endobj 1397 0 obj >/Filter/FlateDecode/ID[99F09C433BA3E74FAFD6B5679B801655>10D0DE9B1FDC084D81D228EB77CDEE20>]/Index[1381 42]/Info 1380 . Substitute the change in strain equation into the strain rate formula and solve the formula using your measured values. The change in strain E would then be equal to E = (L- L0) ÷ (L0 x t). For example if the initial length of the material is 5.0 cm and the material stretched to 6.9 cm in 15 seconds than the strain rate E = (6.9 cm .
ski doo compression test
Strain rate control is one of the most misunderstood parts of common metals testing standards such as ISO 6892-1 and ASTM E8. This video breaks down: what is.Uniaxial tensile tests were conducted using displacement control at three different nominal strain rates, hereinafter called high rate (with average strain rate of 10−1 s−1), intermediate rate (with average strain rate of 10−3 s−1), and low rate (with average strain rate of 10−5 s−1). The plots of instantaneous strain rate versus A novel drop tower modification was designed and implemented in order to enable tensile coupon testing at medium strain rate regime (1–200/s), using a drop weight apparatus, instead of intermediate strain rate servo-hydraulic tensile machines. The developed tensile device, which consists of one movable and one rigid frame, has the ability to transform the . We can observe this behavior using a lower strain-rate test such as a tensile test. Tensile tests apply stress over a significantly longer time scale than impact tests. Instead of a few millisec, tensile tests can last for 30 to 300 sec. But within this longer time envelope we can vary the strain rate by pulling the sample at different rates.
Learn how to conduct a uniaxial tension test, what is it, and why it is important in engineering! View and example lab report with procedure and findings. . strength of elongation is a measurement that can be determined by the change in the length of the specimen after the test has been conducted. The strain rate is the change in deformation . Tensile test results include the ultimate tensile strength, yield strength, Young's modulus, ductility, and the strain hardening exponent. In many cases, the specimen sizes and geometries are . Setup. The tensile test is one of the most important testing methods for characterizing or obtaining material parameters. In the tensile test, for example, it is determined which load a material can withstand until it begins to deform plastically (yield strength) or under which maximum load the material breaks (tensile strength).The tensile test can also be used .
The temperature and strain rate applied during testing can significantly alter the tensile strength and mechanical response of polymers. While ductile plastics or tough polymers exhibit a yield point, many brittle plastics or composites and elastomers do not exhibit a true yield point or proportional limit where a material deformation .
ISO 6892-2 recommends the use of lower strain rates than at room temperature; however in the case of certain applications, i.e. for the comparison with the room temperature tensile test characteristic values at equal strain rate, additional higher strain rates are permitted.
In this example, a tensile test is simulated at four different strain rates. The Johnson–Cook hardening law is used to model the strain rate dependency of the plastic hardening. The temperature distribution and thermal expansion caused by the heating generated by the plastic deformation are also computed. In a separate study, the influence of .
Tensile testing is a fundamental type of mechanical testing performed by engineers and materials scientists in manufacturing and research facilities all over the world. A tensile test (or tension test) applies force to a material .
In the time-independent tensile test a sample of the material called specimen is slowly pulled with axial force until it breaks. The specimen may have a circular or a rectangular cross section and its ends or shoulders are enlarged to provide extra area for gripping (Fig. 1.1).The state of stress in the gripped area is three-dimensional. Ultimate Tensile Stress (UTS) and Ductility. It may be noted at this point that it is common during tensile testing to identify a “strength”, in the form of an “ultimate tensile stress” (UTS).This is usually taken to be the peak . Lindholm et al. [7] conducted tensile tests on AA5454 in annealed and H34 temper conditions. Top hat tensile specimens were used, allowing testing to be conducted using a compressive Hopkinson bar apparatus with strain rates in the range of 1×10 −4 –1×10 3 s −1.Their results showed that the 0.2% offset yield strength was a weak function of strain rate . The potential for the onset of sub-critical crack growth during slow strain rate tensile testing of Monel K-500 immersed in 0.6 M NaCl and exposed to applied potentials ranging from −850 to −1100 mV SCE was systematically evaluated using both H diffusion-based analyses and a new phase field formulation for H-assisted fracture. These efforts .
The ratio of the amount the section has stretched to the original length is called the tensile strain, \begin{equation}\varepsilon_{T}=\frac{\delta l}{l_{0}}\end{equation} Experimentally, for sufficiently small stresses, for many materials the stress and strain are linearly proportional,
Both the load (stress) and the test piece extension (strain) are measured and from this data an engineering stress/strain curve is constructed, Fig.3.From this curve we can determine: a) the tensile strength, also known as the ultimate tensile strength, the load at failure divided by the original cross sectional area where the ultimate tensile strength (U.T.S.), σ max = P max /A 0, .At a temperature of 200°C ( Fig.7c), the steel investigated displays negative strain rate sensitivity of the tensile strength up to strain rates of about 10s -1, due to strain rate dependent microstructural processes (dynamic strain ageing). Hence, for the purpose of establishing constitutive equations, care must be taken when extrapolating or .Higher speed tensile and fracture characterization also aids in predicting the properties of stamped parts, as deformation rates in stamping are 100 to 1,000 times higher than most testing rates. Steel alloys possess positive strain rate sensitivity, or m-value, meaning that strength increases with strain rate. This has benefits related to .
For example, is the strain between times t 1 and t 2 in the figure is 0.5, and the time interval is t 2 - t 1 = 10 years, then the strain-rate is 0.05 1/yr. Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\): Schematic plot showing strain accumulation over time. The slope of the line is the strain rate. Strain rate changes over time and can even be zero. The tensile Testing method measures the force required to break a metallic, composite, or plastic specimen and the extent to which the specimen stretches or elongates to that breaking point. Tensile Test Procedure. A tensile specimen of standard dimensions machined from the metal is inserted in a tensile testing machine (shown in the below figure).
Ambient Tensile Testing of Metallic Materials What Changed? In 2009, ISO 6892-1 replaced and combined both the . standards. It incorporated many changes, but most notably, it introduced the testing rates based on strain rate (Method A). Method A was the recommended approach and was based on maintaining a strain rate. The traditional test .
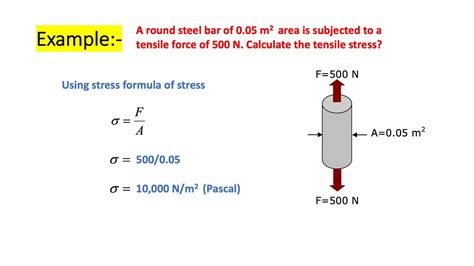
Test specimen may be round or flat in the cross-section. In the round specimens it is accepted, that L 0 = 5 * diameter. The specimen deformation (strain) is the ratio of the increase of the specimen gauge length to its original gauge length: δ = (L – L 0) / L 0. Tensile stress is the ratio of the tensile load F applied to the specimen to .
Resultado da About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features NFL Sunday Ticket
strain rate in tensile test|tensile strength formula and units